Standard procedures for root canal therapy
Root canal therapy refers to that doctors use special instruments for root canal therapy to thoroughly remove infected dental pulp, infected dentin and toxic decomposition products, wash, disinfect and tightly fill root canals, isolate bacteria from entering root canals and reinfection, prevent periapical lesions or promote the healing of periapical diseases.
1、 Pulp opening and decay removing
Before the root canal treatment, the decaying substance must be removed, and then another new turning needle (split drill or emery turning needle is acceptable, but the emery turning needle has less vibration during the pulp opening, and the pulp opening is stable) must be used to enter the pulp cavity. After the pulp cavity is penetrated, the high-speed ball drill must be used to uncover the top, and the top must be completely uncovered, so that the whole pulp chamber bottom can be seen clearly, and then the split drill or emery turning needle can be used to trim the pulp wall.
The standard of quality control in this step is:
① Remove the humus and original fillings.
② Uncover the pulp top and see the whole anatomical structure of the pulp bottom.
③ The pulp wall and root canal wall are continuous and smooth.
④ There are no dental neck steps, no excessive cutting of pulp wall and pulp floor.
2、 Pulp cavity preparation (preparation of upper part of root canal crown)
This step actually includes three contents: preparation of supracoronal segment, dredging of root canal and determination of working length. We usually use three methods to prepare the medullary cavity: standard method, step back method and crown depth method. No matter which method is used, we suggest that the preparation of supracoronal root canal should be placed at the first step of root canal preparation. The following two methods are recommended for supracoronal root canal preparation:
① 10 # k root canal was dredged (dredged to the maximum that 10 # can reach without exceeding the working length), 15 # k root canal was dredged at the beginning of the preparation of the dredged length, GG drill 1 # 2 # 3 # root canal upper section preparation (without the use of a proper).
② 10 # k frustration and dredging and 15 # preliminary preparation are the same as above, and then SX and S1 are used to open the upper segment of the root canal (there are props that use this method, which is less difficult and is not easy to form steps). After opening the upper segment of the root canal, 10 # k frustration is used (of course, the thick root canal is another matter)
3、 Root canal length measurement
The following three methods were used to measure the length of root canal: x-ray method, root measuring instrument and hand feeling method. It is suggested that the root measuring instrument (COXO Johnson Medical Root Measuring Instrument has no difference between personal experience and imported root measuring instrument, accurate measurement data, good stability, and support for domestic products) should prevail.
However, the root tester may be inaccurate under the following three conditions, so it is recommended to take the initial film:
a. Affected teeth with damaged or larger apical foramina.
b. Affected teeth with large root tip shadow.
c. The teeth with residual pulp after an incomplete pulp extraction.
4、 Root canal preparation
The root canal preparation method is nothing more than one of the three methods mentioned above (standard method, step back method, crown depth method) or a combination method. The following types of instruments are commonly recommended: k (10 #~40 #), c (6 #, 8 #, 10 #), G drill, and different preparation methods for two sets of different instruments used by the robot:
① Stainless steel k setback, this set of system routinely uses the gradual retreat method, and the preparation method uses the balance force method.
② The method of gradual penetration is used for the prop instrument. The root canal system is very complex. Any instrument and any method of preparation cannot reach the entire root canal system, so the combination of mechanical preparation and chemical preparation is very important (use the smallest needle as far as possible, move it up and down to flush with light pressure, and prevent the needle from getting stuck).
Preparation of standardized quality control standards:
a. There was no damage in the apical stenosis area, and there was an obvious pause.
b. The main gum tip can reach the length smoothly and has a sense of clamping.
c. The side compressor can reach 1~2mm from the working length.
d. The root canal taper is continuous and the upper segment is open.
e. There was no deviation in preparation, root tip pulled out, lateral penetration, steps, etc.
5、 Root canal disinfection
At present, experts hold different opinions on whether it is necessary to disinfect the root canal after good and thorough mechanical and chemical preparation. Our national conditions are: it is recommended that living pulp teeth or teeth with infection limited to crown pulp can be treated once, and others can be treated with root canal sealing.
At present, there are four categories of sealing drugs recognized by advanced dental and endodontics experts:
a. Calcium hydroxide (including various finished products and prepared products)
b. Iodoform
c. Antibiotics
d. Chlorhexidine. The four categories can be used alone or in combination.
6、 Root canal filling
At the time of filling, there is no conscious symptom, no obvious percussion pain, no odor or exudation in the root canal, and no symptoms of acute periapical inflammation. It is not necessary to wait until all the symptoms disappear. Repeated sealing can easily cause great stimulation to the periapical region. Filling method and quality control standard:
a. The distance between fillings and root tips shall be no more than 2mm.
b. The filling is compact, continuous, and the taper is appropriate.
c. After filling, 2~3 mm below the root canal orifice of the hot gutta percha tip, and the small size obturator is used for cold pressurization.
d. For patients with insufficient filling, it is necessary to prepare filling again, while for those with excessive filling, it is not recommended to do it again in principle. Follow up and perform apical surgery if necessary. Current research shows that under the premise of the same other factors, the prognosis of overcharge is worse than that of underfill.
There are many ways of root canal therapy (root canal preparation and root canal filling). According to the existing knowledge and instruments, a conventional root canal therapy method is set up based on the principles of high quality, fast speed and low consumption.
Root canal therapy includes root canal preparation, root canal irrigation and root canal filling. This section will introduce root canal preparation.
1、 Meaning of root canal preparation
Root canal preparation is to remove and clean the pollutants in the root canal by mechanical means in coordination with chemicals, so that the root canal becomes a certain shape, which is conducive to flushing and filling.
On the basis of the confirmation of the size standard of the pulp opening, the morphology of root canal preparation should be paid attention to (the cheap morphology should keep the morphology resistant morphology).
Ideas of root canal therapy:
(1) It is necessary to predict the number, direction and shape of root canals.
(2) Think of the preparatory steps to be taken.
(3) Think of the final preparatory form.
(4) The equipment shall be fully recognized and selected.
2、 Morphology after root canal preparation
The restoration of tooth defects needs to prepare the residual tooth tissue into a certain shape to facilitate the good retention of the restoration. In order to close the root canal system, root canal filling also requires good shape after root canal preparation.
Conventional concepts of post root canal preparation forms include: (1) inexpensive form. (2) Retention form.
The restoration of tooth defects needs to prepare the residual tooth tissue into a certain shape to facilitate the good retention of the restoration. In order to close the root canal system, root canal filling also requires good shape after root canal preparation.
The conventional concepts of post root canal preparation include:
(1) Convenience form. (2) Retention form
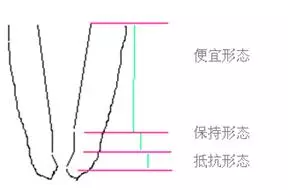
(3) Resistance form.
1. Cheap form
The cheap form is the straight open and dilated cone form with the cutting end or the biting face facing the root tip, which can reduce pollutants pushing out of the root tip hole, and facilitate irrigation, root canal filling and lateral wall pressure.
2. Keep shape
Maintaining the shape is a distance of 1-2 mm within the apical stenosis, which is made by rotary cutting of the enlarger without pulling and cutting against the root canal wall. It is the original shape of the enlarger (nearly parallel). It gives the tester a feeling of tugback when testing the main gum tip.
3. Resistance form
The resistant form is the apical form of root canal preparation, which is naturally cut from the tip of an enlarger or a root canal file at an angle of 75 degrees. The purpose is to prevent the root canal filling material from exceeding the apical aperture, and to make the apical sealing more tight.
(3) Resistance form.
1. Cheap form
The cheap form is the straight open and dilated cone form with the cutting end or the biting face facing the root tip, which can reduce pollutants pushing out of the root tip hole, and facilitate irrigation, root canal filling and lateral wall pressure.
2. Keep shape
Maintaining the shape is a distance of 1-2 mm within the apical stenosis, which is made by rotary cutting of the enlarger without pulling and cutting against the root canal wall. It is the original shape of the enlarger (nearly parallel). It gives the tester a feeling of tugback when testing the main gum tip.
3. Resistance form
The resistant form is the apical form of root canal preparation, which is naturally cut from the tip of an enlarger or a root canal file at an angle of 75 degrees. The purpose is to prevent the root canal filling material from exceeding the apical aperture, and to make the apical sealing more tight.
3、 Medullary foramen
1. The position and size of the normal pulp opening
The left figure shows the size and location of the normal foramen pulposus. The left picture shows the lower jaw, and the right picture shows the upper jaw.
2. Design criteria of pulp opening in root canal therapy
Root canal therapy needs to remove the contents of the pulp cavity (remove the top of the pulp chamber), establish all root canal approaches, and allow a large amount of irrigation fluid. The design standard of the pulp opening is to establish access, so as to establish a good field of vision and operation.
(1) Straight path: a straight path is required for root canal therapy, which can reach one third of the root tip
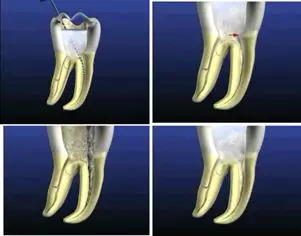
测量标准:以允许根管器械直线并直接进入根尖 1/3 且不接触冠方各壁为标准。
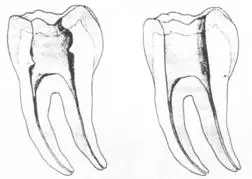
( 2 )髓腔其他改变:如髓室顶、继发性牙本质、修复性或增龄性牙本质。见左图。
右图中有继发性牙本质,切削后获得直线通路。
4、 Root canal preparation steps
The root canal preparation steps include: (1) the use of rubber barrier. (2) There are four X films in total (pre operation, diagnosis wire, confirmation of main gum tip, post operation).
(3) Myelotomy and confirmation of working length (WL). The whole process is unblocked to No. 20 (from 08K-10K, H-15K, H-20K). (4) Preparation of upper segment of root canal (1/3-1/2 of crown). (5) Root canal
Preparation of the middle segment (more than 2mm from the stenosis). (6) Lower segment of root canal (stenosis 2m)
1. Use of rubber barrier
Rubber barrier can prevent infection and accidents. It should be used when conditions permit. The first step in root canal therapy is to use a rubber barrier.
2. X-ray film
There are 4 X ray films in total, including preoperative, diagnostic wire, confirmation of main gum tip, and postoperative.
(1) Preoperative: preoperative X-ray film is used to understand the general condition of teeth. The X-ray film should be taken off the head when multiple teeth are expected before operation.
(2) Diagnostic wire: After preliminary preparation of pulpotomy and root canal according to preoperative X-ray film, diagnostic wire shall be inserted to indicate the position of working instruments. The No. 10 or No. 15 enlarger is usually inserted into the pulp cavity as a diagnostic wire.
(3) Confirmation of main gum tip: through preoperative anticipation and diagnosis with diagnostic wire, determine the working length and root orientation, and prepare the root canal. After that, the main gutta percha point (middle file) should be confirmed to determine whether the root canal is suitable for filling.
(4) Postoperative: observe the therapeutic effect.
3. Working length (WL) measurement
Length measuring instrument and diagnostic wire shall be used to measure the working length to reduce errors.
During the measurement, the root canal needs to be initially dredged in the whole process, gradually dredged from No. 8 instrument to No. 20 instrument, No. 08 K → No. 10 K → 10H → No. 15 K → No. 15 H → No. 20 K. The tip diameter of No. 20 instrument, i.e. root canal working length, is 0.20mm. Then root canal shaping was performed.
4. Preparation of upper root canal
The preparation of the upper part of the root canal (1/3-1/2 of the crown) requires the opening of the root canal orifice. When opening the root canal orifice, use tapered emery or protective tip to shape and open the root canal orifice. It can assist the use of chemicals.
After opening the root canal orifice, use the reamer to make the root canal orifice.
5. Preparation of middle root canal
The middle segment of root canal refers to the area 2mm above the stenosis of root canal. When the root canal is bent, the middle segment refers to the above bending range. The reamer is often used to prepare the middle of the root canal. In addition, there are root canal files, chemicals, etc.
The right figure shows the reamer. The tip diameter of the reamer is the maximum diameter at this location. The commonly used reamers are No.1, No.2, No.3 and No.4, and the corresponding tip diameters are shown in the following table.
| model |
1# |
2# |
3# |
4# |
| Maximum tip diameter |
0.50 mm |
0.70 mm |
0.90 mm |
1.10 mm |
6. Preparation of lower root canal
The lower segment of root canal is the apical segment (the stenosis is 2mm). The preparation of the lower segment of the root canal was performed with a conventional enlarger or a root canal file.
Operation method: The tip shape of the instrument was inserted into the root canal and gently rotated to obtain the tip shape.
7. Working length (WL) reconfirmation
After the preliminary preparation of the root canal, use the H file to lift it, and then confirm the working length. Insert the gutta percha tip, take X-ray, and observe the position of the main gutta percha tip.
Related News






